Key Points
- Tesla demonstrated its Full Self-Driving (Supervised) technology completing a 362-mile journey from San Francisco to Los Angeles with zero human interventions
- The demonstration follows years of gradual improvements in FSD capabilities, with Tesla transitioning from rule-based coding to end-to-end neural networks
- Tesla’s FSD (Supervised) requires constant driver attention and readiness to take control, distinguishing it from fully autonomous systems
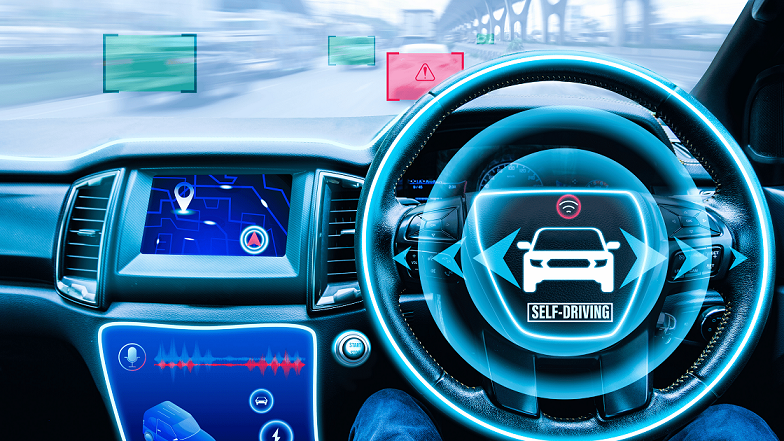
The self-driving battle is on. In a remarkable display of autonomous driving prowess, Tesla recently showcased its Full Self-Driving (Supervised) system completing an impressive 362-mile journey from San Francisco to Los Angeles without requiring a single human intervention. It was an achievement that signaled a pivotal moment in the evolution of self-driving technology and Tesla’s journey toward fully autonomous vehicles.
The demonstration, shared through Tesla’s official channels, featured a Model Y navigating the entire route while the driver remained hands-free, ready to intervene if necessary but never needing to touch the steering wheel.
Understanding Tesla FSD (Supervised)
Tesla FSD (Supervised) represents the current iteration of the company’s autonomous driving technology. Unlike fully autonomous systems, FSD (Supervised) requires an attentive driver who must be prepared to take control at any moment. The system combines advanced computer vision, neural networks, and real-world driving data to navigate complex traffic scenarios.
The technology operates through a sophisticated network of cameras positioned around the vehicle, creating a 360-degree view of the driving environment. These cameras feed information to Tesla’s neural networks, which have been trained on billions of miles of real-world driving data collected from Tesla’s global fleet.
Key Features of FSD (Supervised)
Tesla FSD (Supervised) includes several advanced capabilities that enable autonomous navigation:
- Navigate on City Streets: The system can handle complex urban driving scenarios, including traffic lights, stop signs, and pedestrian crossings.
- Highway Navigation: Advanced lane-changing, merging, and highway interchange navigation capabilities.
- Parking and Summon: Automated parking in various scenarios and the ability to summon the vehicle in parking lots.
- Traffic Control Recognition: Real-time identification and response to traffic signals, signs, and road markings.
The Historic 362-Mile Journey
The recent San Francisco to Los Angeles demonstration represents one of the longest documented zero-intervention drives by Tesla’s FSD system. Tesla aims to demonstrate the reliability of its Full Self-Driving (FSD) Supervised feature and has posted a demo video on X showing a Model Y completing a 362 mile (583km) journey without any human intervention.
This achievement builds upon previous attempts, including earlier demonstrations where Tesla vehicles successfully completed similar routes with minimal interventions. The consistency of these long-distance autonomous drives demonstrates the maturity of Tesla’s FSD technology.
Route Complexity and Challenges
The San Francisco to Los Angeles corridor presents numerous challenges for autonomous driving systems:
- Urban Complexity: Navigating dense city traffic in both San Francisco and Los Angeles metropolitan areas.
- Highway Variations: Multiple highway systems with varying traffic patterns, construction zones, and weather conditions.
- Diverse Driving Scenarios: The route encompasses everything from city streets to rural highways, testing the system’s adaptability.
- Weather and Lighting: Changes in lighting conditions and potential weather variations throughout the journey.
Tesla’s FSD development has shown measurable improvements in key performance indicators. The most critical metric for autonomous driving systems is the distance between interventions—how far the system can drive before requiring human assistance.
Tesla’s safety data provides additional insight into FSD performance compared to traditional driving. Tesla vehicles using Autopilot, including FSD, record one crash per 5.94 million miles driven. Without it, Tesla drivers see one per 1.51 million miles, far better than the U.S. average of one per about 670,000 miles, showing how this tech tenderly enhances safety.
Key Milestones in FSD Development
- 2015: Initial Autopilot launch for adaptive cruise and lane assist.
- 2016: Hardware 2 introduced, with staged self-driving videos.
- 2019: Hardware 3 rollout for enhanced FSD capabilities.
- 2021: FSD Beta version 10.3, though briefly halted for safety tweaks.
- 2025: Latest updates like v12.6.4 and v13.2.9 focus on unified driving stacks and smoother maneuvers.
Technical Evolution: From Code to Neural Networks
Tesla’s approach to autonomous driving has undergone a fundamental transformation. For years, Tesla’s Full Self-Driving (FSD) system was a complex tapestry woven from millions of lines of explicit C++ code. Engineers painstakingly wrote rules for every conceivable driving scenario, but this approach has evolved dramatically.
The current system represents a shift toward end-to-end neural networks that learn from human driving behavior rather than relying on pre-programmed rules. This transition has enabled more natural and adaptable driving behaviors, contributing to achievements like the 362-mile zero-intervention journey.
Training Data Advantages
Tesla’s unique position in the autonomous driving space stems from its access to real-world driving data:
Fleet Learning: Every Tesla vehicle contributes driving data, creating a massive learning dataset.
Diverse Scenarios: Data collection spans various geographic regions, weather conditions, and traffic patterns.
Continuous Improvement: Regular over-the-air updates allow for system-wide improvements based on collective learning.
Edge Case Recognition: The system learns from rare and challenging driving scenarios encountered by the global fleet.
Current Limitations
Despite impressive demonstrations, Tesla FSD (Supervised) has recognized limitations:
Driver Attention Required: The system demands constant driver vigilance and readiness to intervene.
Environmental Challenges: Performance may vary in adverse weather conditions or complex construction zones.
Edge Case Handling: Unusual or unexpected scenarios may still require human intervention.
Geographic Variations: System performance may differ across various regions and road types.
from safety advocates, regulatory bodies, and third-party testing organizations. These concerns highlight the gap between Tesla’s promotional materials and real-world performance.
Criticism and Safety Concerns
Tesla’s FSD technology faces significant criticism from safety advocates, regulatory bodies, and third-party testing organizations. Over 700 reported accidents and 59 fatalities have been linked to Autopilot and FSD systems as of mid-2025.
These concerns highlight the gap between Tesla’s promotional materials and real-world performance.
Federal Investigations and Safety Incidents
The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) opened investigations into Tesla’s Full Self-Driving system following multiple incidents, including a fatal collision with a pedestrian while the FSD feature was active. Regulatory scrutiny includes probes into 2.4 million vehicles after fatal crashes in low-visibility conditions.
Tesla vehicles show a higher accident rate of 26.67 per 1,000 drivers compared to other brands, per LendingTree data.
Despite progress, these concerns underscore the need for further refinements to build public trust.
Third-Party Testing Results
Independent testing has revealed concerning performance gaps. Tesla Full Self-Driving was tested by third-party testing firm AMCI and the result was a ridiculous 13 miles between interventions, highlighting the dramatic difference between controlled demonstrations and real-world performance.
AMCI Testing’s evaluation found Tesla FSD to be “surprisingly capable, while simultaneously problematic (and occasionally dangerously inept)” after testing over 1,000 miles across various conditions. After 300 miles of New York City driving, AMCI Testing’s latest evaluation demonstrates Tesla FSD is clearly not capable of self-driven taxi duty.
Misleading Marketing and Communication Concerns
The NHTSA is investigating Tesla’s FSD software following concerns raised by the automaker’s social media posts, suggesting regulatory concerns about how Tesla presents its technology capabilities to the public.
Safety advocates point to a pattern of overpromising on autonomous capabilities. Tesla has repeatedly provided timeline projections for full autonomy that have not materialized, leading to criticism about misleading consumer expectations.
Addressing the Criticism: Tesla’s Response
Tesla maintains that its safety data demonstrates FSD’s benefits compared to traditional driving. The company argues that focusing on isolated incidents ignores the broader safety improvements achieved through autonomous driving assistance.
The company continues to emphasize that FSD (Supervised) is exactly that—a supervised system requiring active driver attention. Tesla argues that proper use of the system, combined with driver supervision, provides enhanced safety benefits.
The Road Ahead for Tesla FSD
Tesla’s achievement in demonstrating a 362-mile zero-intervention drive from San Francisco to Los Angeles represents a significant milestone in autonomous driving technology.
Looking forward, Tesla plans to introduce unsupervised FSD, allowing fully autonomous operation without oversight. This comes with unique challenges, but Tesla’s continued progress in improving miles between interventions and expanding system capabilities suggests meaningful advancement toward the company’s autonomous driving goals. The combination of extensive real-world data collection, neural network improvements, and continuous over-the-air updates positions Tesla as a strong contender in the evolving autonomous vehicle landscape.
You May Also Like:
The Tesla Diner: A Hit or Miss?
The Lucid, Nuro, and Uber Robotaxi Deal: Everything You Should Know
Is Lucid Motors Outperforming Tesla in Luxury Electric Vehicles and Range?

I’m Dr. Brandial Bright, also known as the AVangelist. As a dedicated and passionate researcher in autonomous and electric vehicles (AVs and EVs), my mission is to educate and raise awareness within the automotive industry. As the Founder and Managing Partner of Fifth Level Consulting, I promote the adoption and innovation of advanced vehicle technologies through speaking engagements, consulting, and research as we progress to level 5 fully autonomous vehicles.