Table of Contents
As the world races towards a greener future, electric vehicles (EVs) have emerged as the poster child for sustainable transportation. With sales projected to reach a staggering 60% of total car sales by 2030, according to the International Energy Agency, the EV revolution is well underway. Indeed, electric vehicles (EVs) have changed the way we drive. They have redefined the transport sector and have emerged as a crucial element in our pursuit of global sustainability.
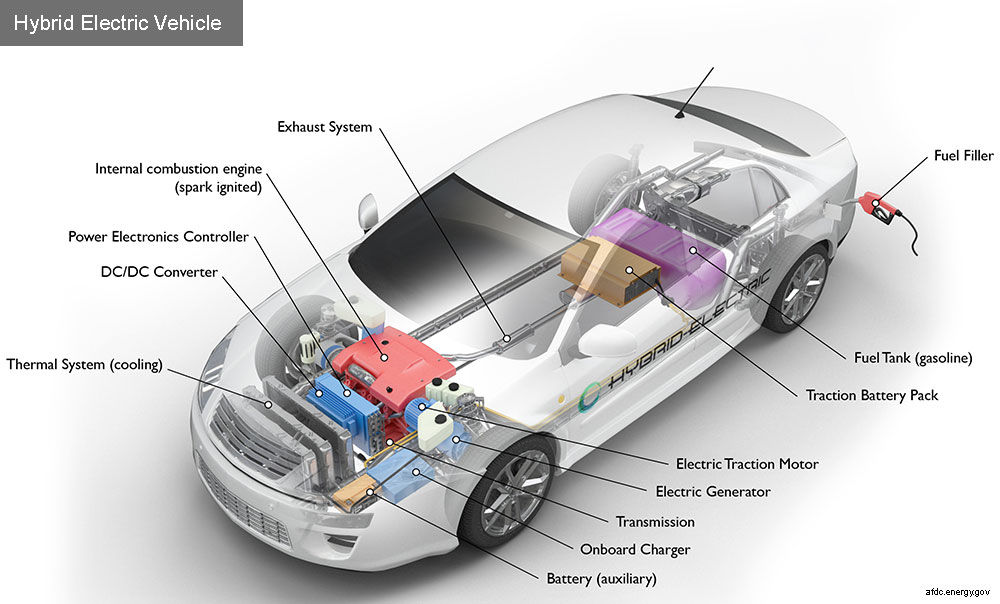
What is an EV and How does It Work?
An electric vehicle (EV) is a car that runs on electricity instead of gasoline. Think, Tesla. It has a large battery that stores the electricity, which is used to power an electric motor. You plug the car into a charging station to refill the battery, just like you charge your phone.
Unlike traditional vehicles that rely on internal combustion engines (ICEs) burning fossil fuels, EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, offering a cleaner and more sustainable transportation option. They can go just as far as gasoline cars on a single charge, and the batteries are getting better all the time.
In 2023 alone, EV sales soared by over 40%, with global sales surpassing 10 million units for the first time.
EVs are typically the preferred choice for AV technology. By producing zero tailpipe emissions, EVs help mitigate carbon dioxide and other harmful pollutants, combating climate change.
Also, EVs contribute to air quality improvement by eliminating emissions of pollutants like nitrogen oxides, particulate matter, carbon monoxide, and volatile organic compounds. This reduction in air pollution positively impacts respiratory health and reduces the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
The noiseless operation of electric vehicles results in reduced noise pollution. This aspect enhances our quality of life, reduces stress levels, and improves sleep patterns for urban residents. EVs can integrate with renewable energy sources, acting as energy storage and promoting efficient utilization of excess energy.
In this article, we’ll take a detailed journey through the key components of electric vehicles (EVs). We’ll explore each part’s function, its contribution to the overall system, and the innovative engineering that brings it all together.
Key Components of Electric Vehicles (EVs)
1. Battery Pack
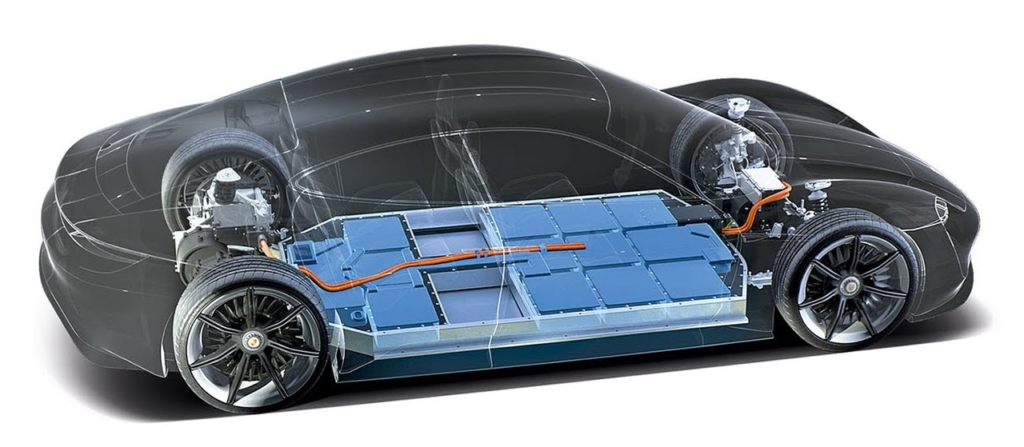

The battery pack is the heart of the electric vehicle. It’s where all the energy needed to drive the car is stored. It’s typically made up of thousands of individual battery cells, which are connected together in series and parallel to achieve the desired voltage and capacity. Most EVs use lithium-ion batteries, similar to those in your smartphone but much larger and more powerful. These batteries are known for their high energy density and long life, enabling EVs to travel hundreds of miles on a single charge. The pack is a sophisticated assembly of individual cells, all meticulously managed to ensure optimal performance and safety.
The battery pack is usually located under the floor of the car, where it is protected from damage.
2. Electric Motor
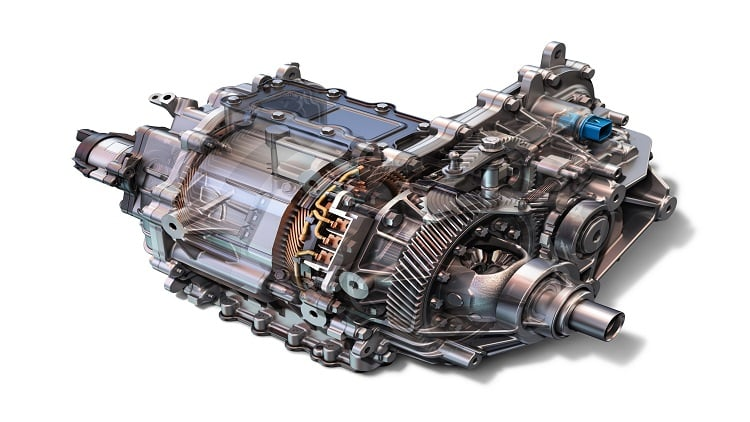
The electric motor converts the electrical energy from the battery into mechanical energy to move the vehicle. There are different types of motors, like induction motors and permanent magnet motors, each with its unique advantages. These motors are incredibly efficient, providing instant torque and smooth acceleration, making driving an EV a delightful experience.
The electric motor is usually located on the front or rear axle of the car.
3. Inverter

Think of the inverter as the brain’s translator. It converts the direct current (DC) from the battery into alternating current (AC) for the electric motor. Additionally, it controls the speed and torque of the motor by adjusting the frequency and amplitude of the AC power. Without the inverter, the smooth and responsive driving experience of an EV wouldn’t be possible.
4. Power Electronics Controller
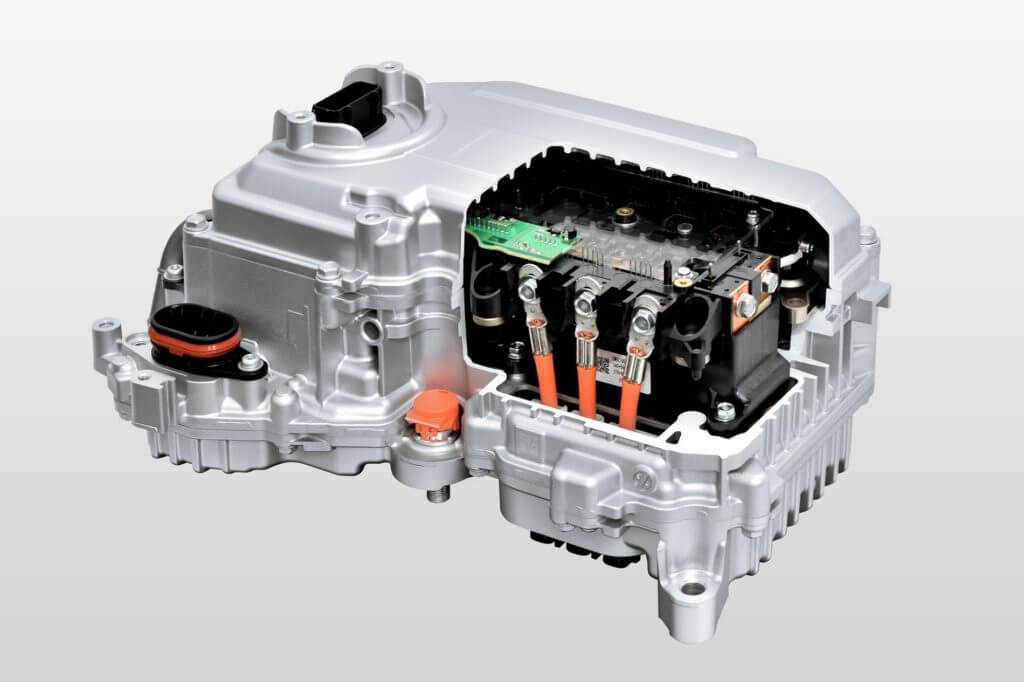
The power electronics controller is like the nervous system of the vehicle. It manages the flow of electrical energy throughout the EV, ensuring efficient distribution from the battery to the motor and other components. This controller ensures that everything works harmoniously, providing a seamless driving experience.
5. Onboard Charger
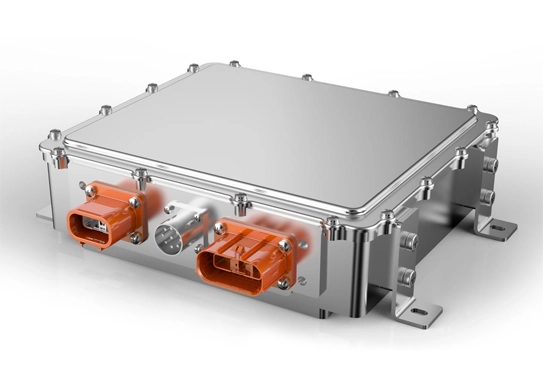
The onboard charger in EVs convert AC power from an external source into DC power to recharge the battery. It manages the charging process to ensure the battery is charged safely and efficiently, whether you’re plugged into a home outlet or a public charging station.
6. Thermal Management Systems
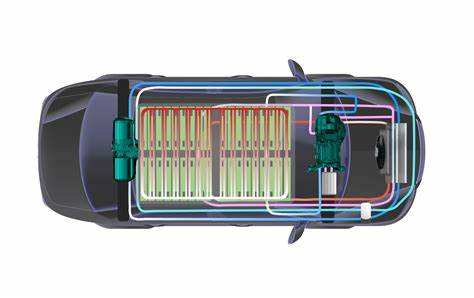
Keeping cool (or warm) is crucial, and that’s where the thermal management system comes in. This system regulates the temperature of the battery pack, motor, inverter, and other components to ensure they operate within safe temperature ranges. It includes cooling and heating mechanisms, such as liquid cooling and heat pumps, to maintain optimal performance.
7. Transmission
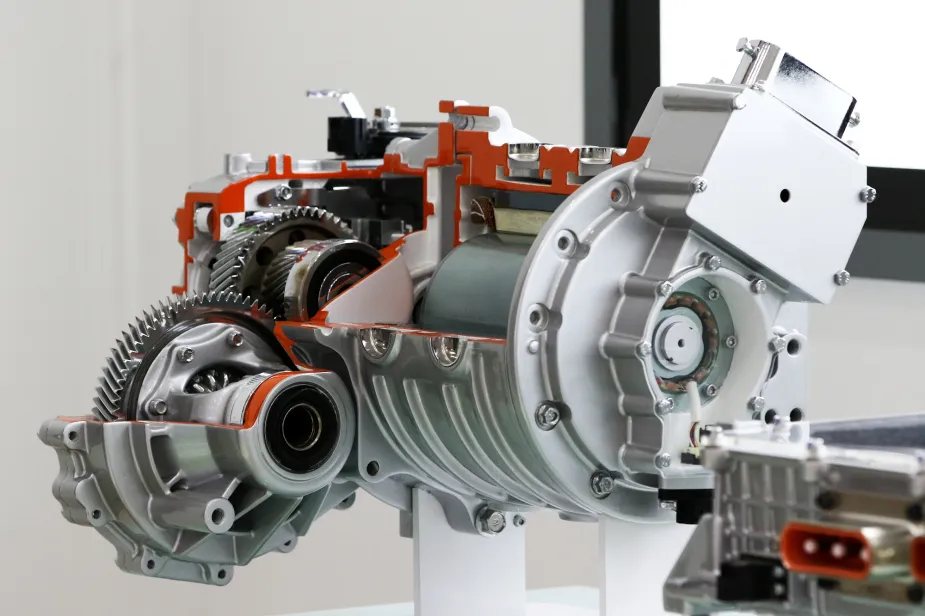
Unlike internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles with multi-speed transmissions, most EVs have a single-speed transmission. This is because electric motors provide instant torque across a wide range of speeds, eliminating the need for multiple gears. However, some high-performance models feature multi-speed transmissions for enhanced efficiency and speed.
The transmission is typically integrated directly with the electric motor, often found on the front or rear axle, depending on the drivetrain configuration.
You May Also Like:
- Driverless Technology: Key Components of Autonomous Vehicles (A Complete Teardown)
- Top 20 Autonomous Vehicle Companies in the U.S. (2025)
8. DC-DC Converter
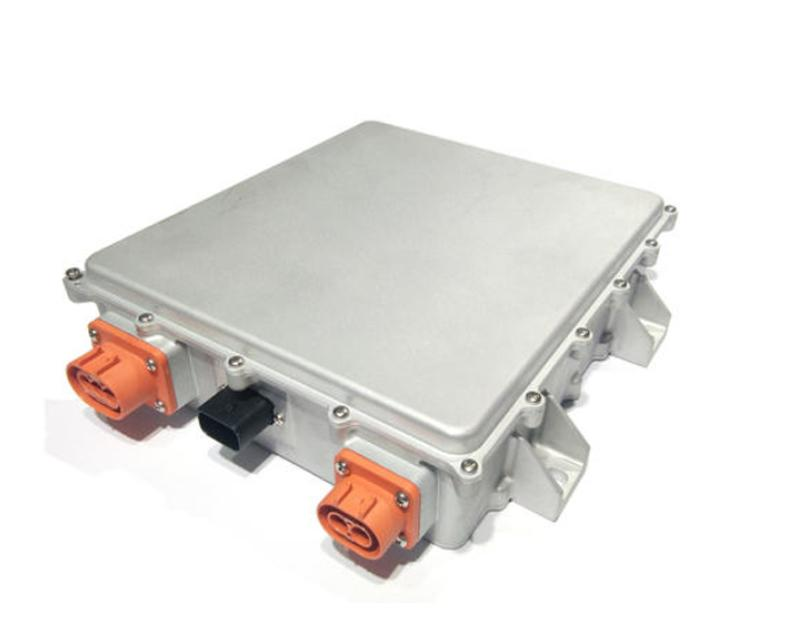

The DC-DC converter converts the high-voltage DC power from the battery pack (e.g., 300-400 volts) to lower-voltage DC power (e.g., 12 volts) to run the vehicle’s accessories like lights, infotainment system, and other electronics.
It is usually found near the battery pack or within the power electronics module.
The DC-DC Converter ensures that all components receive the correct voltage to operate efficiently.
9. Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment (EVSE)
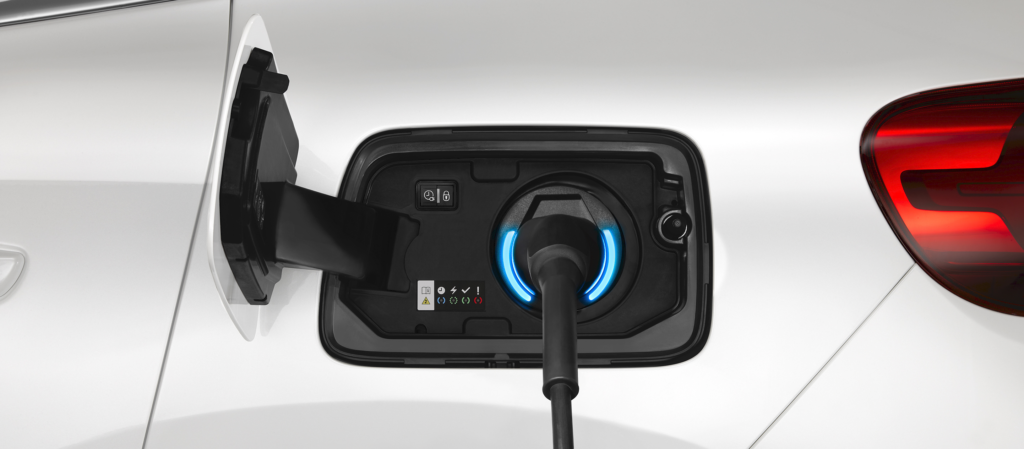

The EVSE, commonly known as the charging station, is the bridge between your vehicle and the power grid. It provides the interface for charging your EV, equipped with safety features like ground fault protection and communication with the vehicle to ensure a safe and efficient charging process. There are different types of EVSE, from Level 1 (slow) to Level 3 (DC fast charging).
EVSE is found at homes, workplaces, public charging stations, and along highways.
10. Charging Port
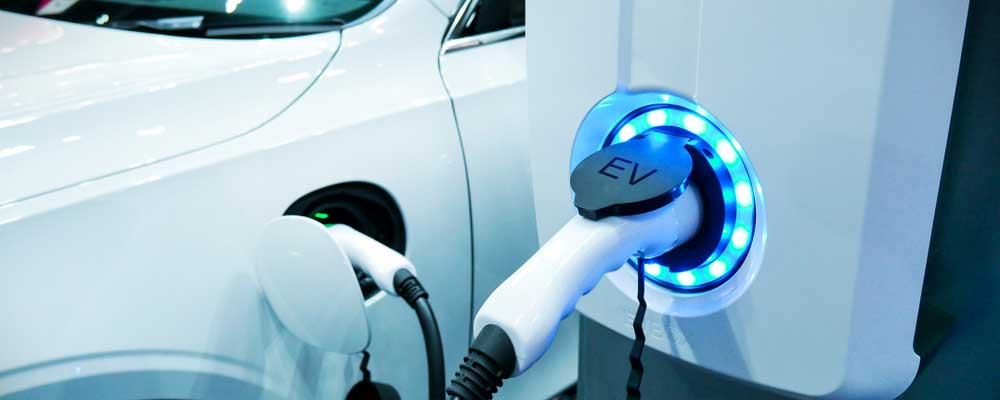

The charging port is the socket that allows the EV to be plugged into an external source of electricity. It is usually located on the side of the car, near the front or rear wheel. The charging port is typically equipped with a safety mechanism that prevents the car from being charged when it is not plugged in.
Various types of charging ports, such as Type 1, Type 2, CCS, and CHAdeMO, support different charging standards and speeds.
11. Battery Management System (BMS)
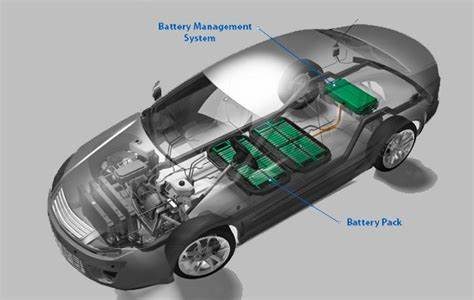
The battery management system (BMS) in EVs is a sophisticated electronic system that monitors and manages the health and performance of the battery pack. It ensures safe operation, optimizes charging and discharging, balances cell voltages, and monitors temperature.
It is usually integrated within the battery pack or placed nearby.
You May Also Like:
- Autonomous Vehicles: The Cruise Debacle and How They Regained Cruise Control
- Case Study: Is South Carolina Ready for Autonomous Vehicles?
12. Regenerative Braking System
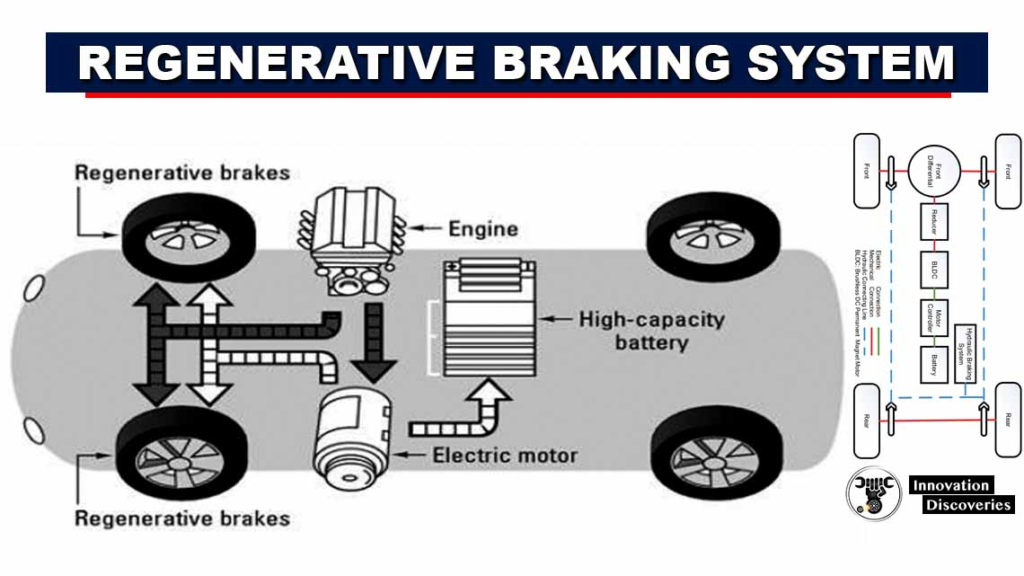
Regenerative braking is one of the coolest features of EVs. This system captures energy that would otherwise be lost as heat during braking and converts it back into electrical energy to recharge the battery. It enhances overall efficiency and can significantly extend the driving range of the vehicle.
The regenerative braking system is integrated into the electric motor and power electronics system.
13. Vehicle Control Unit (VCU)

The VCU is the brain of the EV, overseeing all vehicle functions and systems. It processes input from various sensors and systems to control the motor, battery, thermal management, and other components. It ensures everything runs smoothly and efficiently, delivering a seamless driving experience.
The VCU is typically housed in a secure location within the vehicle, often near the battery pack.
14. Auxiliary Battery
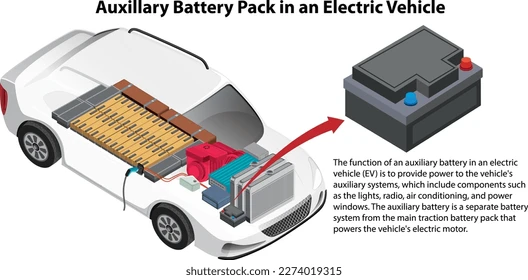
In addition to the main battery pack, EVs usually have a smaller auxiliary battery (often 12V) to power accessories, lighting, and control systems when the vehicle is off or in low-power states. It ensures that essential functions are always available.
The auxiliary battery is usually found in the engine compartment or trunk.
15. High-Voltage Cables
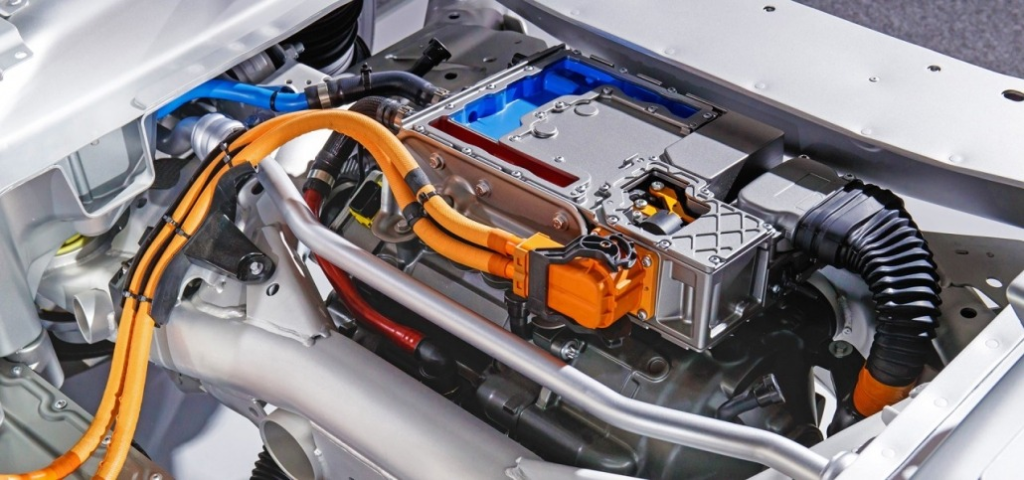

High-voltage cables are the lifelines that connect the battery pack to the inverter, motor, and other high-power components. These cables are designed to handle high current and voltage levels safely, ensuring efficient power transfer throughout the vehicle.
These cables are thick and heavily insulated. They carry high-voltage electricity (300-800 volts) between the battery pack, motor, inverter, and other high-voltage components.
The high-voltage cables are run throughout the vehicle, often protected within conduit or channels under the floor.
16. Telematics and Infotainment System
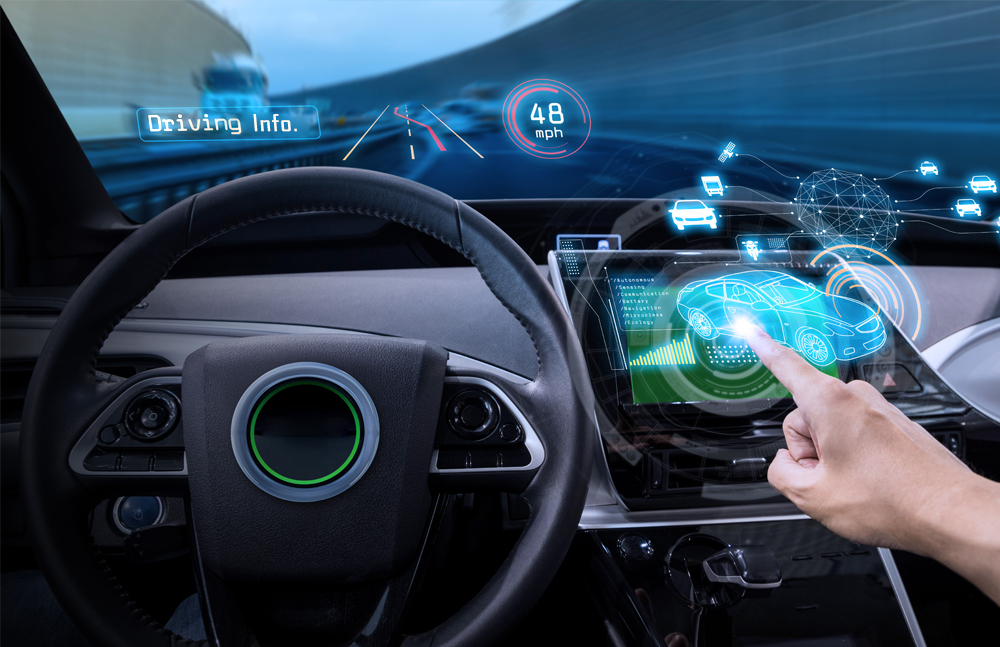

The telematics and infotainment system is your EV’s communication and entertainment hub. It provides navigation, multimedia, and connectivity features, often through a sleek touchscreen display. It keeps you connected, informed, and entertained, making every journey enjoyable.
This component is usually integrated into the dashboard or center console, often featuring a large touchscreen display.
17. Body and Chassis
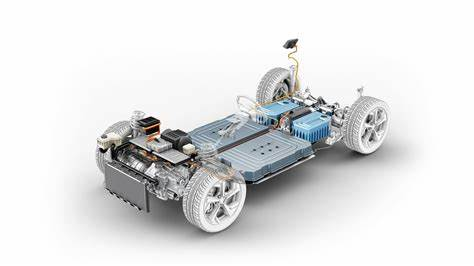
The body and chassis of an EV provide structural support and protection for the components. They are designed to optimize aerodynamics, safety, and weight distribution for improved performance and efficiency. The chassis houses the battery pack, motor, suspension, and other systems.
The body and chassis form the overall structure of the vehicle.
18. Sensors
EV sensors play a pivotal role in monitoring, controlling, and optimizing various aspects of electric vehicles’ performance and safety. From measuring battery health to regulating motor torque, each sensor brings unique functionalities to the EV. The sophisticated sensor technology ensures that your EVs operate smoothly and safely. They are a couple of sensors in EVs, ranging from battery management sensors, temperature sensors, advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) sensors, current and voltage sensors, speed sensors, etc.
Understanding these key components gives us a greater appreciation for the engineering awesomeness that EVs are. They are not just vehicles; they are sophisticated systems designed to provide sustainable, efficient, and enjoyable transportation. As technology continues to evolve, we can look forward to even more advancements in EVs, making them an integral part of our journey toward a cleaner and more sustainable future.

I’m Dr. Brandial Bright, also known as the AVangelist. As a dedicated and passionate researcher in autonomous and electric vehicles (AVs and EVs), my mission is to educate and raise awareness within the automotive industry. As the Founder and Managing Partner of Fifth Level Consulting, I promote the adoption and innovation of advanced vehicle technologies through speaking engagements, consulting, and research as we progress to level 5 fully autonomous vehicles.