Autonomous vehicles (AVs) are the rave of the moment! This technology, once considered a myth, is now a reality. From the streets of San Francisco to the highways in Houston, self-driving cars have taken over, all thanks to the autonomous vehicle companies in the U.S. making this possible.
The excitement and apprehension around this technology is palpable. But the truth is, driverless vehicles have the potential to revolutionize transportation in our society.
AVs are designed to eliminate human error, which is the leading cause of accidents. With advanced sensors, cameras, and AI algorithms, AVs can detect and react to hazards more quickly and effectively than human drivers, potentially reducing accidents significantly.
One of the biggest attractions of this technology is the fact that it can provide transportation to individuals who are unable to drive themselves, such as the elderly, sick, disabled, or those without a driver’s license. This can greatly improve their quality of life and independence.
Autonomous vehicles have many other benefits like reducing traffic congestion, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, creating new business opportunities, and improving economic growth.
The AV market size reached $158.3B in 2023 and could reach $2.3T by 2032. McKinsey predicts that by 2030, vehicles that are fully autonomous will be able to operate “anywhere, anytime” with Level 5 technology, the highest standard of technology available.
As AVs move closer towards mainstream utility, here are the top 20 US autonomous vehicle powering this driverless cutting-edge technology:
Table of Contents
1. Waymo

Year Founded: 2009
Location: Mountain View, CA
Funding: $2.5B Series B funding
Value: Estimated to be over $30 billion
Key Facts: Waymo began as a secret. The project was started by Sebastian Thrun, who led his robotics team with Stanford University to win the DARPA Grand Challenge.
Waymo is considered a leader in developing autonomous driving technology. Its cars have now logged more than 10 million miles on public roads. Additionally, Waymo has completed over 250,000 paid ride-hailing trips in a week in three major cities: San Francisco, Phoenix, and Los Angeles. It has planned expansions into Austin, Miami, Florida, and Washington DC.
2. Tesla

Year Founded: 2003
Location: Austin, Texas
Funding: Public company, funding through public markets
Valuation: Market cap over $600 billion
Key Facts: Tesla is a pioneer in the development of advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) called Autopilot. This technology is one of the most well-known semi-autonomous driving systems on the market. Autopilot runs on Level 2 automation, as defined by SAE International.
Tesla’s CEO Elon Musk has stated that Tesla plans to commence rollout of its Level 5 autonomous vehicles, the Cybercab, later this year. The branding for this beta testing program is known as “Full Self-Driving (FSD).”
According to the company, the Full Self-Driving capability is a pre-release upgrade package to Autopilot offering additional ADAS features, such as traffic light recognition, autopark, etc.
Elon Musk is not a fan of the LiDAR technology and does not plan to use it in its Full Self-Driving capability vehicles. Rather, Tesla’s approach to try to achieve SAE Level 5 is to train a neural network using the behavior of 6+ million Tesla drivers using chiefly visible light cameras and the coarse-grained two-dimensional maps used for navigation.
3. Zoox
Year Founded: 2014
Location: Foster City, California
Funding: Acquired by Amazon
Valuation: Acquired for over $1.2 billion
Key Facts: Zoox is Amazon’s independent and subsidiary autonomous vehicle company. It aims to create autonomous mobility from the ground up, with a focus on ride-hailing services.
The Zoox vehicle is bidirectional, meaning it can travel in either direction without turning around. It has no steering wheel or pedals, and the interior is designed for face-to-face seating.
Zoox utilizes a comprehensive sensor suite, including cameras, LiDAR, and radar, to provide 360-degree awareness of its surroundings. The AV brand prioritizes safety in its design and development process. They have conducted extensive testing in various environments.
As a subsidiary of Amazon, Zoox has access to significant resources and expertise.
Zoox became the first company to self-certify a purpose-built, fully autonomous, all-electric passenger vehicle to Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards (FMVSS), a significant milestone.
4. Aurora Innovation

ear Founded: 2017
Location: Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania
Funding: Publicly traded (Nasdaq: AUR) with significant investments from Amazon, Sequoia, and others
Valuation: Market cap fluctuates (check current stock price)
Key Facts: Aurora Innovation was co-founded by former heads of Google, Tesla, and Uber’s self-driving divisions. Their core technology is the Aurora Driver, a self-driving computer system designed to be adaptable to multiple vehicle types (trucks, passenger cars, etc.)
Aurora Innovation prioritizes safety through rigorous testing, redundancy in systems, and a phased approach to deployment, starting with highway trucking. They utilize extensive simulation and virtual testing environments to accelerate development and ensure safety before real-world deployment.
Aurora Innovation has had collaborations with major automakers like Toyota, Volvo, and PACCAR to integrate the Aurora Driver into their vehicles.
You May Also Like:
Case Study: Is South Carolina Ready for Autonomous Vehicles?
5. Kodiak Robotics

Year Founded: 2018
Location: Mountain View, California
Funding: Over $500 million from investors like Bridgestone Americas, BMW, iVentures, and others
Valuation: Not publicly disclosed, but estimated in the hundreds of millions
Key Facts: Kodiac Robotics exclusively focuses on the development of autonomous technology for long-haul trucking.
Unlike many AV companies, Kodiak relies primarily on cameras and radar, minimizing the use of expensive LiDAR sensors. They believe this approach is more scalable and cost-effective for commercial deployment.
Kodiac developed a proprietary mapping system called “lightweight mapping” that requires less detailed mapping data than competitors, allowing for quicker expansion into new routes.
They are collaborating with major trucking companies like Werner Enterprises and U.S. Xpress to test and deploy their technology.
Kodiac recently launched the sixth-generation Kodiak Robotics Inc. self-driving truck that does not need a safety driver in the autonomous semi-truck.
Kodiac trucks have carried 5000+ loads over more than 2.5 million miles.
6. May Mobility

Year Founded: 2017
Location: Ann Arbor, Michigan
Funding: $166 Million from various investors including Toyota
Valuation: Not Publicly Disclosed
Key Facts: May Mobility focuses on providing autonomous shuttle services for specific routes, often in partnership with public transit agencies. Their driverless fleet has provided over 320,000 public rides around the world since its first route in 2019.
May operates in urban, suburban, and rural environments, showcasing the adaptability of their technology. Their AVs are ommitted to accessibility, with all fleets including wheelchair-accessible vehicles.
May has a Proprietary Multi-Policy Decision Making (MPDM) system, which enables vehicles to virtually simulate thousands of scenarios per second to make safe decisions.
7. Gatik

Year Founded: 2017
Location: Palo Alto, California (with operations in Texas and Canada)
Funding: $120+ million from Koch Disruptive Technologies, Wittington Ventures, Innovation Endeavors, and others
Valuation: Not publicly disclosed
Key Facts: Gatik is focused exclusively on autonomous middle-mile logistics for the B2B retail industry. This means they automate the transport of goods between distribution centers, dark stores, and retail locations.
Gatik’s AVs operate on fixed, repeatable routes, which simplifies the technological challenge and allows them to achieve higher levels of reliability. The company has successfully deployed its autonomous trucks in several states, partnering with major retailers like Walmart and Loblaw Companies Ltd.
8. Nuro

Year Founded: 2016
Location: Mountain View, CA
Funding: Over $2.1 billion from Softbank, Woven Capital, Kroger, and others in funding over 7 rounds
Valuation: Estimated at over $8.6 billion (as of 2023)
Key Facts: Nuro develops electric, fully autonomous vehicles for local goods delivery, not passenger transportation.
They design and manufacture their own compact, electric delivery vehicles (R1 and R2) specifically optimized for local deliveries.
Nuro has partnered with major retailers like Kroger, Domino’s, Walmart, and FedEx for pilot delivery programs. They are the first company to receive a permit from the U.S. Department of Transportation to deploy autonomous delivery vehicles on public roads.
Regarding safety, Nuro emphasizes features like external airbags and a low speed design.
Nuro is also building autonomous vehicles for ride-hailing services.
9. Beep

ear Founded: 2019
Location: Lake Nona, Florida
Funding: Private, with investments from various partners
Valuation: Not publicly disclosed
Key Facts: Beep, Inc. is a leading provider of autonomous and electric shared mobility solutions. Their shuttles provide transportation within specific areas, connecting residents and visitors to key destinations.
Beep utilizes NAVYA’s Autonom Shuttle vehicles for its operations. It has successfully deployed its autonomous shuttle services in several locations, including Honolulu’s international airport, Lake Nona in Florida, Mississippi University, Yellowstone National Park, etc.
Beep’s focus on first- and last-mile transportation in planned communities sets it apart from companies targeting broader autonomous vehicle applications.
10. Motional
Year Founded: 2020
Location: Boston, MA
Funding: Acquired/Merged, last deal amount $923M
Valuation: Not publicly disclosed
Key Facts: A joint venture of Hyundai and Aptiv. Motional is one of the most established players in the robotaxi space, with a strong track record of public deployments. The company combines Hyundai’s expertise in vehicle manufacturing with Aptiv’s experience in advanced safety technologies and autonomous driving systems.
Motional has partnered with major ride-hailing companies like Lyft and Uber to offer robotaxi services in multiple cities.
Safety is a core value for Motional, with rigorous testing and validation procedures to ensure the reliability of their autonomous systems. To date, Motional has provided over 100,000 self-driving rides with zero at-fault accidents on its record.
Motional is actively expanding its robotaxi services to new cities around the world.
11. Mobileye

Year Founded: 1999
Location: Jerusalem, Israel (U.S. operations in Detroit, MI and San Diego, CA)
Funding: Publicly traded (Nasdaq: MBLY); IPO in October 2022 raised approximately $861 million
Valuation: Approximately $28 billion as of Q1 2025
Key Facts: A global leader in computer vision and autonomous driving technologies, Mobileye began as a pioneer in advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and has evolved into a powerhouse in the AV sector. Now a subsidiary of Intel, Mobileye leverages cutting-edge AI, crowdsourced mapping, and scalable driving policy software to support both driver-assist and full autonomy.
Mobileye’s robotaxi platform, Mobileye Drive™, is designed for Level 4 autonomy and is being deployed through partnerships with companies like Sixt, Volkswagen, and Zeekr.
The company emphasizes a “responsibility-sensitive safety” (RSS) model, which underpins its autonomous decision-making and risk management framework. As of Q1 2025, Mobileye’s autonomous vehicles have driven millions of cumulative miles in pilot programs across the U.S., Germany, and Israel—with plans to expand further across urban and suburban environments.
Mobileye continues to bridge the gap between assisted and autonomous driving, positioning itself as a key player in the global rollout of robotaxis and self-driving systems for commercial fleets.
12. Nvidia

Year Founded: 1993
Location: Santa Clara, California
Funding: Public company, funding through public markets
Valuation: Market cap approximately $300 billion as of 2021
Key Facts: Nvidia is not directly building autonomous vehicles. They are a leading provider of artificial intelligence (AI) chips and software that power the complex computing systems needed for self-driving cars.
Nvidia is a pioneer in AI and deep learning, and they leverage this expertise to create algorithms for AV perception, decision-making, and path planning.
Their DRIVE platform is a comprehensive solution for AV development, encompassing hardware (SoCs, GPUs), software (DRIVE OS, Drive AV, Drive IX), and infrastructure (DRIVE Constellation). It provides the computational horsepower and software tools necessary for perception, mapping, planning, and control.
Nvidia’s DGX systems provide the data center infrastructure required for training and fine-tuning deep learning models for AVs.
Nvidia collaborates with numerous automakers, tier-1 suppliers, and software developers to integrate its technology into various AV platforms. Some notable partners include Mercedes-Benz, Volvo, Toyota, and Hyundai.
13. AutoX

Year Founded: 2016
Location: San Jose, CA
Funding: Series B, total funding over $160M
Valuation: Not publicly disclosed
Key Facts: AutoX is a leading autonomous driving technology company focused on fully driverless robotaxi deployment. The company was founded by Dr. Jianxiong Xiao (a.k.a. Professor X), a former Princeton professor and computer vision expert. AutoX’s technology emphasizes full-stack, camera-first autonomy supported by lidar and radar systems for redundancy and safety.
AutoX was the first company to deploy a fully driverless robotaxi fleet in China and is one of the few to have received permits for driverless operation in California. It has launched autonomous pilot programs in multiple international markets, including the U.S., China, and Europe.
Safety and scalability are at the core of AutoX’s operations, with the company conducting millions of miles of road testing and simulation annually. AutoX’s robotaxis have completed over 250,000 autonomous rides globally, with zero reported at-fault accidents in fully driverless mode.
The company is actively pushing toward Level 5 autonomy and expanding its operational domains through collaborations with municipal governments and mobility-as-a-service platforms.
14. Luminar Technologies

Year Founded: 2012
Location: Orlando, Florida
Funding: Publicly traded (LAZR)
Valuation: Approximately $2.5 billion (as of June 2024)
Key Facts: Luminar focuses solely on developing and manufacturing high-performance LiDAR sensors, a crucial component for AV perception systems. Their LiDARs are known for their long range, high resolution, and ability to detect objects in challenging conditions like rain, fog, and darkness.
Unlike many LiDAR startups focused on R&D, Luminar is delivering production-ready LiDARs that are being integrated into vehicles by major automakers. This has earned them partnerships with Volvo, Daimler Trucks, and SAIC Motor, among others.
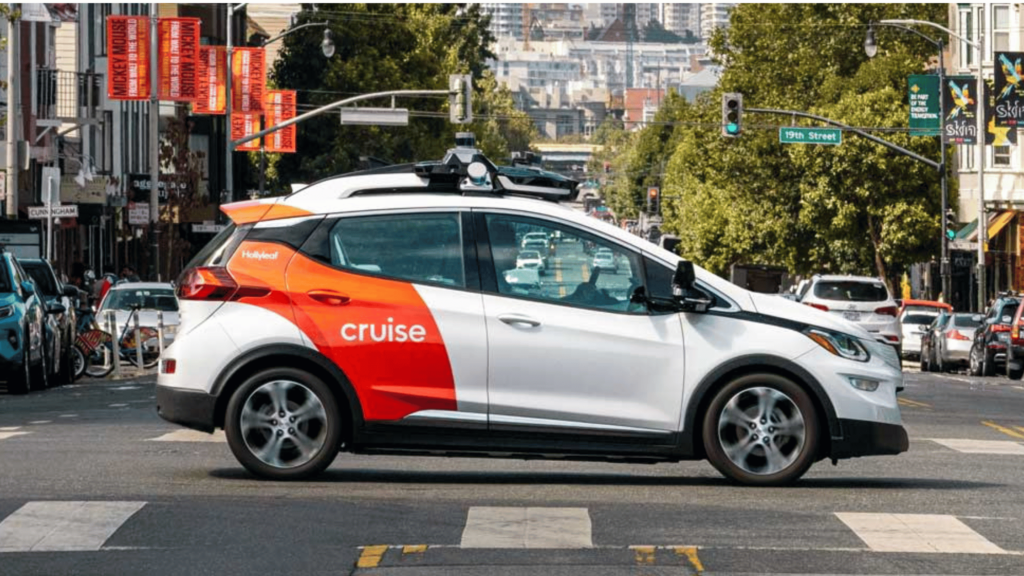
15. Cruise

Year Founded: 2013
Location: San Francisco, California
Funding: Majority-owned by General Motors, with investments from Honda, Microsoft, and others.
Valuation: Estimated at $30 billion
Key Facts: Cruise is a pioneer in the development of custom self-driving vehicles without steering wheels or pedals. The AV company, once into on developing robotaxi services for urban environments, is now focused on integrating its Cruise Driver autonomous technology into vehicles.
Cruise lost its operational license in California due to series of crashes and complaints. The most talked about being an accident that saw a Cruise robotaxi inadvertently hit and drag a female pedestrian for about 20 feet about halting on a sidewalk. This happened in October 2023. After losing its license, Cruise suspended operations and recalled all its driverless fleet.
As of 2025, Cruise is no longer actively making custom-built autonomous vehicles for urban transportation.
You May Also Like:
- The Cruise Debacle and How They Regained Cruise Control
- Driverless Technology: Key Components of Autonomous Vehicles (A Complete Teardown)
16. Nexar

Year Founded: 2015
Location: New York City, New York
Funding: $135 million+ in total funding from investors including Ibex, Alibaba, Nationwide, State Farm Ventures, and others.
Valuation: Not publicly disclosed
Key Facts: Nexar is not primarily an autonomous vehicle (AV) company. Rather, they focus on utilizing artificial intelligence and dash cam technology to improve road safety and the driving experience.
Nexar uses AI to analyze dash cam footage for accidents, hazards, and road conditions. They also provide valuable data to cities, insurers, and fleet managers to improve safety.
In a nutshell, Nexar contributes to the broader AV ecosystem through data and insights.
17. Ouster

Year Founded: 2015
Location: San Francisco, California
Funding: Publicly traded (NYSE: OUST)
Valuation: Market cap around $200 million (as of June 2024)
Key Facts: Like Luminar, Ouster is a leading provider of high-resolution LiDAR sensors, a critical component for AV perception.
Their LiDAR sensors use a unique digital architecture that offers several advantages over traditional analog LiDAR, including lower cost, higher resolution, and greater reliability.
Ouster has partnered with several leading AV companies, including Waymo, Ike, and Yandex, to provide LiDAR sensors for their self-driving systems.
18. Pony.AI

Year Founded: 2016
Location: Fremont, California (with major operations in China)
Funding: Over $1.2 billion from investors like Toyota, Ontario Teachers’ Pension Plan, and others.
Valuation: Estimated at over $8.5 billion (as of April 2023)
Key Facts: Pony.ai operates and tests robotaxi services in both the U.S. (California) and China (Beijing, Guangzhou, Shanghai). They developed a “Virtual Driver” system that simulates human-like driving behavior for realistic testing and validation.
Pony.ai is known for its advanced self-driving technology stack, including perception, prediction, planning, and control algorithms. They collaborate with Toyota to develop and deploy robotaxis, leveraging Toyota’s manufacturing expertise and Pony.ai’s software.
In May 2022, Pony.ai had its permit revoked by the California DMV for failing to monitor the driving records of the safety drivers on its testing permit. As of June 2023, Pony.ai has resumed testing its fleet with safety drivers present in California.
19. Nauto

Year Founded: 2015
Location: Palo Alto, CA
Funding: Venture Capital-backed, last known funding round: $159M total raised
Valuation: Estimated at $1 billion+ (as of latest funding rounds)
Key Facts: Nauto is an AI-powered driver behavior and fleet safety platform focused on improving road safety and preventing collisions in commercial fleets. Unlike companies that focus on full autonomy, Nauto leverages predictive AI and computer vision to assist human drivers and reduce risk in real time.
The platform is used by a wide range of commercial fleets across logistics, delivery, and service industries to monitor distractions, drowsiness, and risky driving behaviors.
Nauto’s system has analyzed over 1.3 billion driving miles and helped prevent over 80,000 collisions, according to company data.
While not a robotaxi provider, Nauto plays a key role in the AV ecosystem by bridging today’s assisted driving technologies with tomorrow’s autonomous future. Its work is critical in improving driver safety, reducing insurance claims, and gathering edge-case data useful for AV development.
20. Cavnue

Year Founded: 2020
Location: Washington, D.C.
Funding: Series A; last disclosed funding round raised approximately $130M
Valuation: Not publicly disclosed
Key Facts: Cavnue is a subsidiary of Sidewalk Infrastructure Partners, incubated with support from Alphabet’s Sidewalk Labs. The company is pioneering the development of connected and autonomous vehicle (CAV) corridors, aiming to create infrastructure that supports safe and efficient deployment of AVs at scale.
Cavnue’s mission is to bridge the gap between AV technology and public infrastructure by building intelligent roadways that facilitate communication between vehicles, sensors, and traffic management systems. Its flagship project, the Michigan Connected Corridor, spans a planned 40-mile stretch between Detroit and Ann Arbor and is being developed in partnership with the Michigan Department of Transportation, Ford, and other automotive leaders.
Cavnue emphasizes a public-private collaboration model, ensuring that infrastructure development aligns with government policy, transportation equity, and technological standards. The company is also working with global automakers, transit agencies, and freight operators to future-proof mobility infrastructure.
With its infrastructure-first approach and deep partnerships across sectors, Cavnue is positioning itself as a key enabler in the scalable rollout of autonomous and connected vehicle systems.
Conclusion
These US autonomous vehicle companies represent the zenith of self-driving excellence. They are a mirror showcasing how far autonomous vehicles have come, how much they have accomplished, and what lies ahead.
Experts predict that the autonomous car market will have a value of approximately $196.97 billion by 2030. This is a big leap from it’s 2021 global market size, which stood at $25.14 billion.
As regulators and cities get more comfortable with this technology, there is no limit to what AVs can achieve.
Keep your eyes peeled on the road, you might just see an AV driving by.

I’m Dr. Brandial Bright, also known as the AVangelist. As a dedicated and passionate researcher in autonomous and electric vehicles (AVs and EVs), my mission is to educate and raise awareness within the automotive industry. As the Founder and Managing Partner of Fifth Level Consulting, I promote the adoption and innovation of advanced vehicle technologies through speaking engagements, consulting, and research as we progress to level 5 fully autonomous vehicles.