Nvidia’s meteoric rise to fame is nothing short of astounding. This automotive powerhouse chipmaker grew from a video game graphics company to an AI giant dominating the semiconductor market.
Founded in 1993, Nvidia initially captured attention with its revolutionary GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) technology, transforming the gaming industry with lifelike graphics and unmatched processing power. This led to lucrative deals with Microsoft’s Xbox and Sony’s PlayStation.
Today, however, the company is a leader in much more than just gaming. Nvidia’s technology has redefined industries ranging from automotive and healthcare to data centers and autonomous machines.
Nvidia’s influence is perhaps most keenly felt in the world of autonomous vehicles, where its DRIVE platform has become the backbone for many car manufacturers’ self-driving technologies.
Whether it’s developing AI supercomputers, building virtual simulation environments for AV testing, or powering the world’s largest AI-driven data centers, Nvidia is constantly pushing the boundaries of what’s possible.
In this article, we dive into ten intriguing things to know about Nvidia—how it rose to prominence, the pivotal moments in its history, and the cutting-edge technologies it continues to develop.
From powering the future of self-driving cars to revolutionizing AI research, Nvidia’s journey is one of bold innovation, relentless ambition, and an ever-expanding vision of the future.
Key Facts About Nvidia (Things to Know)
Here are ten key facts about Nvidia:
1. Amazing Origin Story
Nvidia was founded in 1993 by Jensen Huang and his co-founders Chris Malachowsky and Curtis Priem. The name “Nvidia” is derived from the Latin word “invidia,” meaning envy, reflecting the company’s aspiration to create superior graphics technology.
Nvidia is a trillion-dollar company, but its origin story would make you giggle.
Did you know that Nvidia’s founder, Jensen Huang, used to be a dishwasher at a Denny’s restaurant in San Jose, California? It was at this location (over a meal) that Huang and his co-founders met and conceived the idea for Nvidia.
Huang is an Oregon State University and Stanford University electrical engineering graduate. He credits his success as a CEO to his work ethic, which he proudly admitted to have acquired during his early career working minimum wage jobs. During a speaking engagement, Huang claimed he has worked just as hard as a corporate employee as he did cleaning toilets in the past — and he made sure the audience knew that it was a lot of toilets.
Sequioa Capital was Nvidia’s pioneer investor. Huang presented the Nvidia idea to his previous employer Wilfred Corrigan, then-CEO of LSI Logic, who called it “one of the worst elevator pitches he’s ever heard,” according to Huang’s account. However, Corrigan still convinced the founder of Sequoia Capital, Don Valentine, to invest in Nvidia due to Huang’s strong work ethic.
The rest, they say, is history.
Nvidia is headquarted in Santa Clara, California.
2. Graphics Processing Units (GPUs) Market Dominance

One of the keys to Nvidia’s massive success is that it controls about 80% of the market for graphic processing units (GPUs), which are specialized chips that provide the kind of computing power required for services such as Microsoft-backed OpenAI’s wildly popular ChatGPT chatbot.
In 1999, Nvidia introduced the GeForce 256, which is considered the first true GPU. It was notable for its ability to handle transformations and lighting calculations on the chip itself, revolutionizing graphics processing
Graphics processing units (GPUs) are specifically designed to efficiently handle the types of calculations crucial for AI computing, unlike general-purpose central processing units (CPUs) from companies like Intel, which manage a broader set of tasks but with less efficiency.
As AI reshapes the tech landscape, specialized chips like GPUs are gaining prominence. According to Gartner, GPU usage in data centers is expected to grow significantly, from under 3% in 2020 to more than 15% by 2026.
3. Nvidia’s DRIVE: End-to-End Autonomous Vehicle Development Platform

Nvidia was one of the first companies to see the potential of AI in the automotive sector. This gave birth to Nvidia’s DRIVE platform, which serves as a comprehensive suite for developing autonomous vehicles. It integrates hardware and software solutions that enable real-time perception, decision-making, and control.
According to Nvidia, the NVIDIA DRIVE® platform consists of both the AI infrastructure and in-vehicle hardware and software to deliver everything needed to develop autonomy at scale. This platform includes powerful GPUs and AI algorithms tailored for automotive applications.
Interestingly, they began developing their DRIVE PX platform for self-driving cars as early as 2015, positioning themselves ahead of competitors. DRIVE PX is an AI computing platform that allows vehicles to understand the surrounding environment.
Nvidia’s DRIVE platform also helps build redundancy and diversity into the autonomous vehicle–optimizing occupant, pedestrian, and vehicle safety. They have partnered with strong automotive companies and AV startups including Toyota, Hyundai, Volvo, BMW, Mercedes, Cruise, Zoox, TuSimple, Nuro, etc.
4. Nvidia’s CUDA: A Blessing for AI Developers

Nvidia has cultivated a robust ecosystem that integrates software solutions like CUDA, enabling developers to harness the full potential of its chips. CUDA (Compute Unified Device Architecture) is Nvidia’s parallel computing platform and application programming interface (API). With CUDA, software developers can use Nvidia’s GPUs (Graphics Processing Units) to accelerate general-purpose computing tasks.
You May Also Like:
- Top 20 Autonomous Vehicle Companies in the U.S.
- 10 Things Autonomous Vehicles Can Do that Humans Drivers Can’t
5. Omniverse Replicator: Nvidia’s Digital Twin Technology Powering AV Simulation Testing

Nvidia’s Omniverse Replicator is a unique virtual simulation engine where developers can create, simulate, and test autonomous driving scenarios in a photorealistic, physically accurate virtual world. According to Nvidia, autonomous vehicles and robots developed using this data can master skills across an array of virtual environments before applying them in the real world.
In its first implementations of the engine, the company introduced two applications for generating synthetic data: one for NVIDIA DRIVE Sim™, a virtual world for hosting the digital twin of autonomous vehicles, and another for NVIDIA Isaac Sim™, a virtual world for the digital twin of manipulation robots.
This synthetic-data-generation engine was built to produce physically simulated data for training deep neural networks. Autonomous vehicles are simply robots that operate in the open world, striving to avoid contact with anything. And this is where Nvidia’s Omniverse Replicator comes into play. It helps AV companies create digital testing environments for AVs and/or robocars before launching into real-world highways.
The Omniverse Replicator is an invaluable data-generation engine for NVIDIA’s DRIVE technology.
6. Nvidia’s Metropolis is Powering Smart City Technology
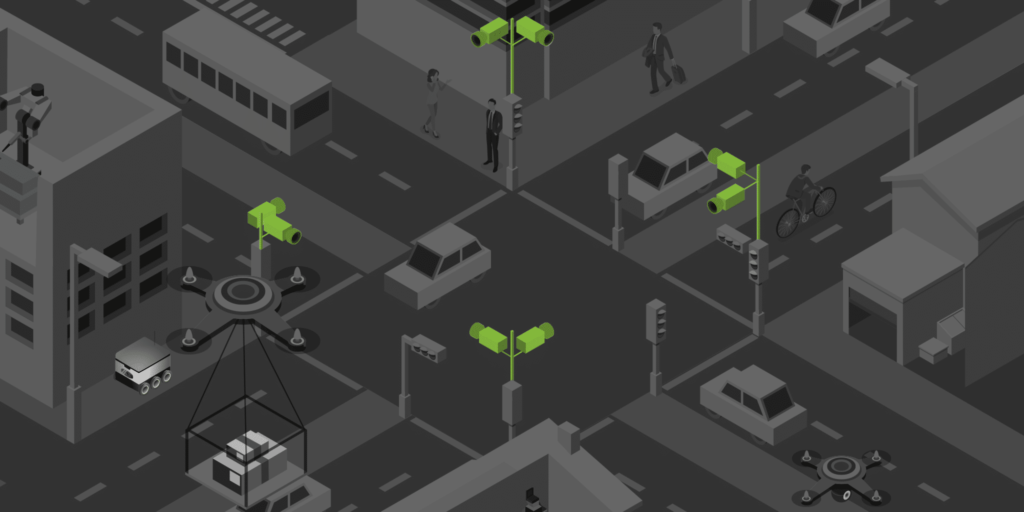
Nvidia’s Metropolis platform can help build a smart city by utilizing AI to process data from sensors, cameras, and IoT devices across urban infrastructure. This data enhances public services like traffic management, environmental monitoring, and public safety. Metropolis can optimize traffic flows by analyzing vehicle and pedestrian movement, reducing congestion, and improving transportation efficiency.
Nvidia’s Metropolis can help build a smart city that communicates effectively with self-driving cars. Metropolis can communicate with AVs in real-time, providing vital information about road conditions, traffic signals, and pedestrian activity. This interaction ensures safer navigation for AVs while allowing cities to operate more efficiently and sustainably.
The platform helps AVs respond to dynamic urban environments by creating an interconnected system where AVs and city infrastructure are in constant communication, leading to smoother traffic and safer streets.
7. Nvidia’s DRIVE Thor: Next-Gen AI for AVs

Nvidia’s DRIVE Thor is an advanced computing platform designed for autonomous vehicle technology. It serves as a centralized computer that combines various functions needed for driving, such as automated driving, parking assistance, and in-car entertainment, all into one system. This integration simplifies vehicle design by reducing the number of separate electronic control units typically found in cars, which can lead to lower costs and lighter vehicles.
The DRIVE Thor chip boasts impressive performance capabilities, reaching up to 2,000 teraflops. This level of processing power allows it to handle complex tasks efficiently, including real-time monitoring of drivers and passengers, as well as managing advanced driver-assistance systems.
Nvidia’s DRIVE Thor is expected to be released in 2025. It will provide the hardware and software necessary for fully autonomous vehicles.
8. Nvidia Only Designs but does not Manufacture their Chips

Did you know that Nvidia designs its chips but outsources the manufacturing to companies like Samsung and TSMC (Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company)?
Nvidia focuses on designing the architecture and functionality of its GPUs and AI chips, but it doesn’t own fabrication plants (fabs) to produce them at scale. Instead, Nvidia contracts TSMC, the world’s largest semiconductor foundry, and Samsung to handle the production. TSMC has been a long-standing partner for Nvidia’s advanced nodes, while Samsung handles certain production lines, depending on the specific chip design and requirements. This outsourcing strategy allows Nvidia to focus on innovation in chip design while relying on industry leaders for high-precision manufacturing.
9. Bryan Catanzaro: The Face Behind Nvidia’s Pivot to AI?

Bryan Catanzaro, Vice President of Applied Deep Learning Research at Nvidia, is credited as the face behind Nvidia’s elevated focus on AI. He started as an Nvidia intern while in graduate school at the University of California, Berkeley. He later rose to the ranks as a research scientist before departing to work at Baidu on AI-based speech recognition. He returned to Nvidia in 2016.
In a LinkedIn post, Catanzaro insisted that he “didn’t actually convince Jensen,” instead he just explained deep learning to him. He instantly formed his own conviction and pivoted Nvidia to be an AI company.”
10. Top Seven Largest Publicly Traded U.S. Firms by Market Cap

Nvidia (NVDA) has joined the prestigious class of the top seven largest publicly traded U.S. firms by market capitalization. With a staggering market capitalization of over $3.3 trillion, Nvidia overtakes Microsoft (MSFT) currently sitting on a $3.04 trillion market cap to become the second largest company in the world, behind Apple (AAPL).
Joining Nvidia in the prestigious group of seven are Apple, Microsoft, Alphabet, Amazon, Meta, and Berkshire Hathaway.
Conclusion
Nvidia’s journey from a graphics processing company to a leader in artificial intelligence and automotive technology is nothing short of remarkable. As we’ve explored above, Nvidia has made significant strides in various sectors, particularly with its groundbreaking innovations like the DRIVE, which promises to revolutionize the way vehicles operate and interact with their environments.
Echoing the sentiments of Jensen Huang, Nvidia’s CEO, “The era of AI has begun, and Nvidia is at the center of this revolution.”
Nvidia’s GPUs, pivotal in AI computing, are expected to dominate data centers, with Gartner predicting specialized chips like GPUs to power over 15% of data centers by 2026, up from just 3% in 2020.
The automotive industry is taking notice. Partnerships with major players like ZEEKR, Hyundai, Volvo, Toyota, Cruise, Zoox, etc., demonstrate a growing recognition of Nvidia’s potential to enhance vehicle intelligence and safety. Industry stats also project that by 2025, over 50 vehicle models will utilize Nvidia’s DRIVE technology.
As we look ahead, it is clear that Nvidia will continue to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of transportation and beyond.
Related:
- Ten Amazing Things to Know About Waymo in 2024
- 10 Intriguing Things to Know About GM’s Cruise
- 10 Interesting Things to Know About Kodiak Robotics in 2024
- Ten Things to Know About Aurora Innovation in 2024
- Understanding ADAS in Autonomous Vehicles and How It Works
- 10 Things You Should Know About Zoox After 10 Years Building Autonomous Vehicles

I’m Dr. Brandial Bright, also known as the AVangelist. As a dedicated and passionate researcher in autonomous and electric vehicles (AVs and EVs), my mission is to educate and raise awareness within the automotive industry. As the Founder and Managing Partner of Fifth Level Consulting, I promote the adoption and innovation of advanced vehicle technologies through speaking engagements, consulting, and research as we progress to level 5 fully autonomous vehicles.