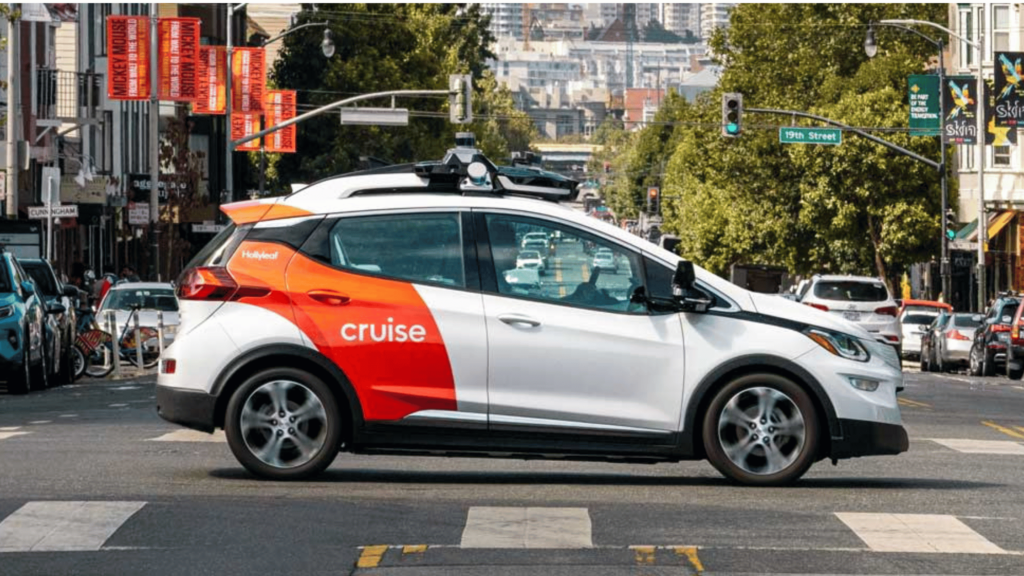
The autonomous vehicle (AV) industry is evolving at a rapid pace, with 2025 set to be a defining year for self-driving technology. We are witnessing advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), sensor technology, and connectivity. AVs are transitioning from experimental prototypes to real-world applications.
From ride-hailing services deploying fully autonomous fleets to regulatory bodies adapting to the challenges of self-driving technology, the industry is experiencing a paradigm shift. Companies such as Waymo, Zoox, Tesla, and Aurora Innovation are leading the charge, pushing the boundaries of autonomy and safety.
Advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), in-cabin monitoring, and vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication are making semi-autonomous driving more reliable and widespread.
According to a Statista report, by 2025, the global autonomous vehicle market is projected to reach $62 billion, growing at an annual rate of over 20%. Additionally, Level 2 and Level 3 autonomous vehicles are expected to account for nearly two-thirds of new car sales, signaling a move toward safer and smarter transportation.
This article discusses the top 10 autonomous vehicle trends for 2025, exploring the latest breakthroughs, challenges, and what lies ahead for the industry.
1. Increased Levels of Automation
By 2025, we can expect a significant expansion in the availability of Level 3 (L3), Level 4 (L4), and Level 5 (L5) autonomous driving capabilities, particularly in private passenger cars. These systems will allow vehicles to handle more complex driverless tasks, such as highway driving or navigating through difficult urban environments. Major automakers are actively developing these technologies, making them increasingly accessible to consumers.
For example, Waymo has officially partnered Uber to roll out driverless taxis in Atlanta, GA. In no distant time, the need for human drivers in traditional ride-hailing platforms like Uber and Lyft will no longer be required.
2. Artificial Intelligence Integration
AI will play a crucial role in enhancing the capabilities of autonomous vehicles. Advanced algorithms will improve object detection, decision-making, and route optimization. Companies are also exploring generative AI for real-time data processing and predictive analytics, which will help vehicles adapt to changing conditions on the road.
For example, Nvidia’s Thor processor, formally known as the “NVIDIA DRIVE Thor” system-on-a-chip (SoC), is a significant advancement in the realm of automotive AI computing. Unveiled at CES 2025, Thor is designed to be the brain behind next-generation autonomous vehicles (AVs), offering unprecedented computational power for real-time processing of sensor data, which is critical for autonomous driving.

“The Thor chip, with 20 times the processing power of its predecessor (Drive ORIN), integrates data from sensors like cameras, radars, and Lidars to enable real-time autonomous navigation and serves as a universal robotics computer for various applications,” Huang noted during his keynote address.
3. Enhanced Vehicle Connectivity
In 2025, we will witness the integration of vehicle-to-everything (V2X) in many cities across the world. This technology will enhance communication between autonomous vehicles, infrastructure, and other road users. V2X connectivity is essential for improving navigation, traffic management, and overall road safety. IoT-enabled sensors will allow vehicles to gather and analyze data in real-time, facilitating timely decision-making.
4. Blockchain Adoption
In 2025, blockchain will play a vital role in autonomous technology. The adoption of self-driving cars relies on processing vast amounts of data efficiently and securely. Blockchain, with its decentralized ledger and cryptographic security, enhances data management by enabling faster, tamper-proof transactions. Its distributed network ensures real-time access to accurate data, improving vehicle tracking, communication, and connectivity.
Additionally, blockchain-powered smart contracts streamline processes such as insurance claims, repairs, and toll payments by automating transactions. Beyond security and efficiency, blockchain also facilitates data-sharing incentives in vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) and vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) communication.
With blockchain-based solutions, drivers and vehicle owners can even monetize their data by selling it to manufacturers in exchange for rewards.
5. Growth in Autonomous Vehicle Production
Annual production of self-driving cars is expected to reach 14.5 million units by 2025, a significant increase from a few thousand in 2020. This surge reflects the rapid adoption of AV technology driven by safety, environmental, and technological factors.
For example, Tesla is planning to mass-produce the Cybercab (its futuristic robotaxi) in 2025. The Tesla cybercab prototype was unveiled at the Tesla “We, Robot” event in Los Angeles on October 10, 2024. According to Tesla, the future of autonomy and artificial intelligence will be realized through the creation of a fleet of autonomous vehicles and robots.
6. Development of Autonomous Delivery Services
Beyond passenger transport, autonomous vehicles are revolutionizing the logistics sector by enabling faster, safer, and more cost-effective deliveries. In 2025, more companies will actively invest in driverless delivery vans, autonomous robots, and drones to streamline supply chain operations and meet the growing demand for e-commerce fulfillment.
Major players like Amazon, Walmart, FedEx, and Nuro are leading the charge, testing and deploying self-driving delivery vehicles that can navigate urban and suburban environments with minimal human intervention.
For example, Nuro’s compact, electric autonomous delivery pods are already operational in select U.S. cities, delivering groceries and takeout meals without requiring a driver. Similarly, FedEx has been testing autonomous delivery robots that can handle last-mile logistics, reducing reliance on human couriers.
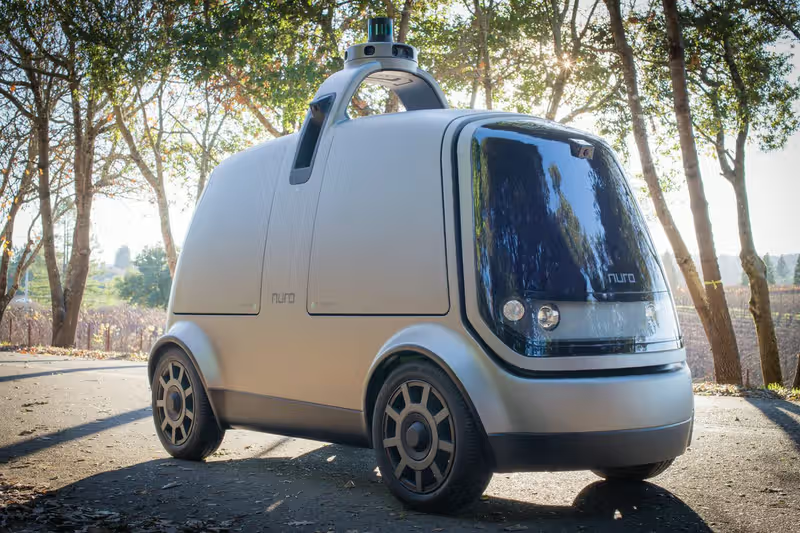

Walmart has entered partnerships with Gatik and Aurora Innovation to optimize middle-mile and last-mile autonomous deliveries.
7. Cybersecurity Measures
As autonomous vehicles (AVs) become more integrated with smart infrastructure, cloud computing, and real-time data exchanges, the importance of cybersecurity cannot be overstated. The increasing connectivity exposes AVs to a wide range of cyber threats, from data breaches and ransomware attacks to vehicle hijacking and GPS spoofing. A single vulnerability in a self-driving car’s system could lead to catastrophic consequences, putting passengers, pedestrians, and entire transportation networks at risk.
In 2025, manufacturers and tech firms will ramp up investments in advanced cybersecurity frameworks. Multi-layered security strategies, including end-to-end encryption, intrusion detection systems, and AI-driven threat monitoring, will be implemented to detect and neutralize threats in real-time. Blockchain technology may also play a pivotal role in securing vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) and vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) communications, ensuring data integrity across networks.
Additionally, governments and regulatory bodies are expected to establish stringent cybersecurity standards for AVs. Compliance with industry regulations, such as ISO/SAE 21434 for automotive cybersecurity and UNECE WP.29, will become mandatory, pushing manufacturers to adopt proactive security-by-design approaches. Over-the-air (OTA) software updates will further enhance protection, allowing automakers to deploy security patches remotely without requiring vehicle recalls.
8. Regulatory Support for Autonomous Driving
Government regulations play a crucial role in shaping the future of autonomous vehicles, balancing innovation with safety and public interest. In 2025, the Trump-led U.S. government is taking significant steps to accelerate the development and deployment of self-driving technology by easing AI-related regulations. This initiative aims to remove bureaucratic hurdles that have historically slowed progress in the AV industry while ensuring robust safety frameworks remain in place.
Key stakeholders, including policymakers, industry leaders, and consumer advocacy groups, are working together to create legislation that fosters technological advancements without compromising safety. For example, discussions around updating the Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards (FMVSS) are gaining traction, particularly concerning requirements that assume a human driver is always in control.
Additionally, states like California, Texas, and Arizona—hotbeds for autonomous vehicle testing—are expected to implement more structured policies to support commercial AV deployments. These regulatory shifts will enable companies such as Waymo, Tesla, and Cruise to expand their self-driving fleets, bringing AV technology closer to mainstream adoption.
9. Sustainability Focus
Sustainability will remain a core pillar in the automotive industry as manufacturers seek to reduce their environmental impact. This includes not only the proliferation of electric autonomous vehicles but also the adoption of green manufacturing processes aimed at minimizing emissions and resource consumption during production.
Automakers are shifting toward sustainable production by integrating renewable energy sources such as solar and wind into their manufacturing plants. Companies like Tesla and BMW are already utilizing solar-powered gigafactories to reduce reliance on fossil fuels. Additionally, advancements in material science are leading to the increased use of recycled and biodegradable components in vehicle production, cutting down waste and reducing carbon footprints.
As electric autonomous vehicles become mainstream, the industry is tackling the challenge of battery waste. Manufacturers are developing second-life programs to repurpose used EV batteries for energy storage in homes and power grids.
The sustainability focus is not just on the vehicles themselves but also on the infrastructure supporting them. Smart charging stations powered by renewable energy, wireless inductive charging, and solar-powered roadways are being explored to reduce emissions further.
10. The Rise of Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS)
The automotive industry is shifting towards a servitization model where companies offer mobility as a service (MaaS). This trend reflects changing consumer preferences towards access over ownership, leading to new business models that incorporate AVs into shared mobility solutions.
Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) is a concept that integrates autonomous vehicles (AVs) into shared mobility solutions such as ride-hailing, car-sharing, and autonomous shuttle services. Companies like Waymo and Zoox are already deploying AVs in pilot programs, offering on-demand rides without human drivers.
Also, Tesla plans to integrate the Cybercab into its ride-hailing app, allowing owners to generate income by offering rides when their vehicles are not in use. Tesla will take a commission of 25-30% from these rides, providing a potential revenue stream for owners while making the service more accessible to consumers.
As autonomous technology matures and regulatory frameworks evolve, fully driverless fleets are expected to become more widespread, reducing reliance on personal vehicles.
Conclusion
In 2025, the autonomous vehicle (AV) industry will undergo a major transformation, driven by technological advancements, regulatory shifts, and evolving consumer expectations. From the expansion of Level 2 and Level 3 autonomy to the deployment of fully autonomous ride-hailing services (Level 5), the industry is witnessing rapid progress in multiple areas.
A key takeaway from these trends is the increasing integration of artificial intelligence, advanced driver assistance systems, and vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication. These innovations not only enhance safety and efficiency but also bring us closer to the reality of full autonomy. However, challenges remain. Cybersecurity concerns, ethical considerations, and the need for a robust legal framework will continue to shape the trajectory of self-driving technology.
Looking ahead, the widespread adoption of autonomous vehicles will depend on how well industry players address safety concerns, consumer trust, and economic feasibility. While full autonomy remains a long-term goal, the advancements anticipated in 2025 will lay the foundation for a more connected, efficient, and intelligent transportation ecosystem.
Ultimately, the next phase of autonomous vehicle evolution is not just about removing human drivers from the equation—it’s about reshaping mobility to be safer, smarter, and more accessible for everyone.

I’m Dr. Brandial Bright, also known as the AVangelist. As a dedicated and passionate researcher in autonomous and electric vehicles (AVs and EVs), my mission is to educate and raise awareness within the automotive industry. As the Founder and Managing Partner of Fifth Level Consulting, I promote the adoption and innovation of advanced vehicle technologies through speaking engagements, consulting, and research as we progress to level 5 fully autonomous vehicles.