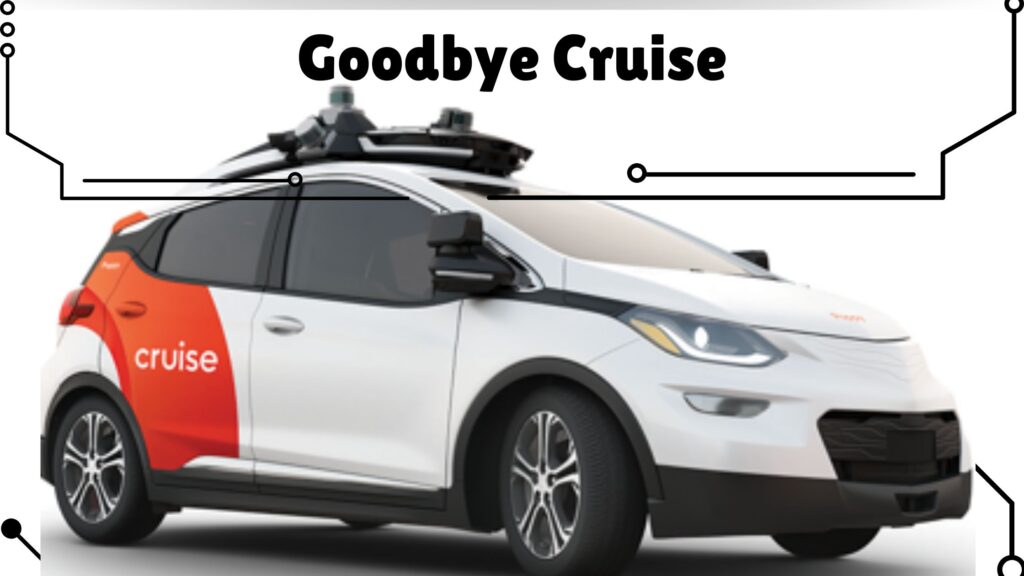
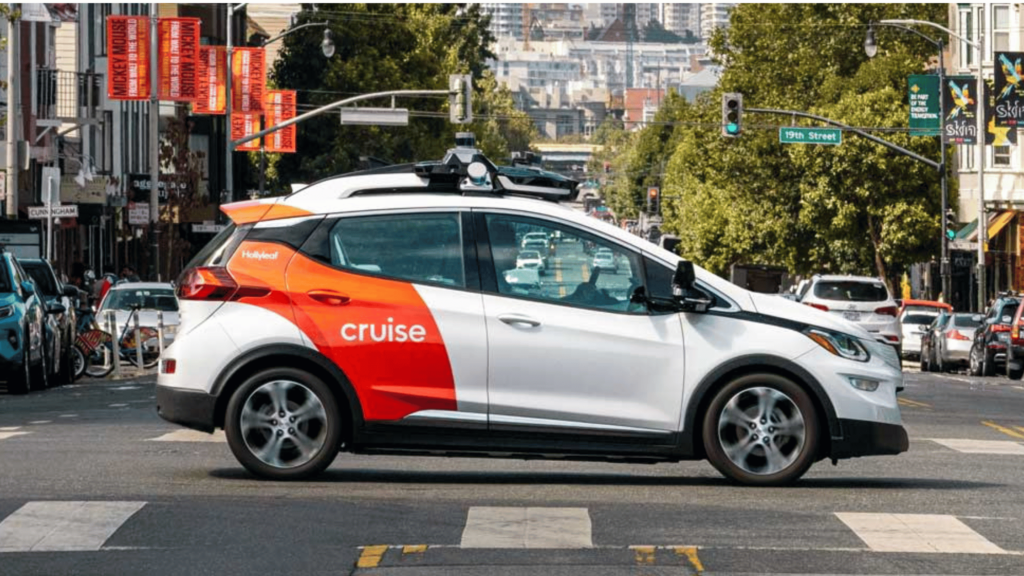
On Tuesday, December 10, 2024, General Motors (GM) announced it would stop funding its Cruise robotaxi project. The Detroit EV automaker cited the excessive cost associated with growing a robotaxi business and the increasingly competitive robotaxi market as major reasons for shutting down Cruise. This bold move has rocked the autonomous vehicle industry.
General Motors (GM) acquired Cruise Automation in March 2016, marking a significant step in its strategy to develop autonomous vehicle technology. Although the exact amount was not disclosed, estimates suggest GM paid “over $1 billion” for the acquisition, with some reports indicating figures ranging from $580 million to more than $1 billion. At the time of acquisition, the young startup Cruise, founded by Kyle Vogt and Dan Kan, had around 40 employees and had raised about $20 million in venture capital.
GM allowed Cruise to remain responsible for technology and commercialization, giving Cruise independence to avoid common pitfalls when a large company acquires a technology startup.
Cruise received a permit to test self-driving vehicle technology (Level 4-5 AVs) from the California Department of Motor Vehicles in June 2015, and from then on, things appeared to be going just fine.
However, things started going downhill for Cruise when its robotaxis started getting involved in a series of crashes. In late 2023, a serious accident involving one of Cruise’s autonomous vehicles raised safety concerns and led to regulatory scrutiny. This incident resulted in the suspension of Cruise’s operating license in California.
In 2024, Cruise slowly resumed testing its driverless cars on city streets in California. However, this time, with a human driver at the steering wheel—a safety requirement from the authorities. Along the line, Cruise struck a partnership deal with Uber, as they slowly started regaining public trust.
However, serious losses coupled with the increasingly competitive robotaxi market forced GM to reassess its commitment to the robotaxi project, joining the likes of Ford and Volkswagen, who stopped funding their robotaxi project, Argo AI.
What are the Numbers Saying?
By December 2024, GM reported that Cruise had incurred over $10 billion in operating losses since its acquisition, generating less than $500 million in revenue during that period.
In 2023 alone, Cruise incurred significant losses totaling approximately $3.48 billion.
GM says shutting down Cruise will save $1 billion in annual losses.
Mary Barra, the Detroit-based manufacturer’s chief executive, had previously predicted that the Cruise business could generate $50bn (£39bn) in annual revenue by 2030.
What Next for GM and Cruise?
Following the decision to shut down its Cruise robotaxi project, General Motors (GM) plans to concentrate on developing fully autonomous vehicles designed for personal use rather than ride-hailing services. This shift aims to leverage advancements in driver assistance technologies, particularly the Super Cruise system, which allows hands-free driving on certain highways. This is similar to Tesla’s “Full Self-Driving” (FSD) model.
GM will enhance the Super Cruise feature, which is currently available on over 20 vehicle models and accumulating more than 10 million miles of usage monthly. The company aims to improve this technology further through ongoing advancements in artificial intelligence and other relevant fields.
Additionally, GM intends to merge the Cruise division with its technical teams, creating a unified effort to advance both autonomous and assisted driving technologies. This integration is expected to streamline operations and facilitate knowledge sharing between teams.
Waymo, Zoox Race Ahead
The recent decision by General Motors (GM) to shut down its Cruise robotaxi project has significant implications for the autonomous vehicle landscape, particularly as competitors like Waymo and Zoox continue to advance their own initiatives.
Waymo, a subsidiary of Alphabet, continues to thrive in the autonomous vehicle sector. As of late 2024, it has achieved significant milestones, including providing over 150,000 rides per week without a safety driver in certain areas. Waymo has expanded its operations into Los Angeles and Austin and is preparing to cover the entire San Francisco peninsula.
Waymo’s vehicles have been reported to have a safer operational record compared to human drivers, with an average of one minor police-reported crash every 10,000 rides. This safety performance positions Waymo favorably as it builds consumer trust in its autonomous services.
A recent report showed that Waymo’s market share is now equal with Lyft in San Francisco, an incredible milestone for an autonomous vehicle company.
When Waymo launched in August 2023, Uber and Lyft were at 66% and 34% shares in SF, respectively.
15 months later, in November 2024, Waymo is at 22%—the same as Lyft—with Uber at 55%.
Related:
Autonomous Vehicles: 10 Amazing Things to Know About Waymo
On the other hand, Zoox, as of November 2024, has begun testing its unique robotaxis in San Francisco, marking its entry into a second commercial market. The company has identified specific neighborhoods, including SoMa near Union Square and Oracle Park, for initial testing of its driverless rides.
This follows a history of testing in the city since 2017, albeit with drivers present until now. CEO Aicha Evans confirmed that Zoox’s bespoke driverless robotaxi has successfully passed all necessary safety measures to commence tests without safety drivers.
Related:
10 Things You Should Know About Zoox
Tesla Gradually Making Its Mark
Tesla is gradually making its mark in the autonomous vehicle (AV) market, particularly with the introduction of its Cybercab robotaxi.
Tesla unveiled its Cybercab robotaxi prototype at the “We, Robot” event in October 2024. The Cybercab is designed without traditional controls such as a steering wheel or pedals, featuring a unique two-seat layout with butterfly doors.
The Cybercab will rely on artificial intelligence and cameras for navigation, avoiding the use of lidar technology that many competitors employ. Musk has expressed confidence in the safety of Tesla’s self-driving technology, claiming that autonomous vehicles could be “10 to 20 to 30 times safer than a human” driver.
Also, Elon Musk stated that the Cybercab would be priced under $30,000, with production expected to begin before 2027.
Related:
10 Fascinating Things to Know About the Tesla Cybercab
Conclusion
From all indications, the autonomous vehicle market is expensive. However, it is predicted to rake in rewards in the near future. By 2028, the AV market could reach approximately $221.32 billion, indicating a robust demand for safer and more efficient transportation solutions.
The AV market is relentlessly pursuing safety and efficient transportation. Autonomous vehicles promise to reduce accidents caused by human error near to zero, thereby enhancing overall road safety.
Continuous advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), sensor technology, and connectivity are improving the performance and safety of autonomous vehicles. These innovations are critical for developing reliable self-driving systems that can operate in diverse environments.

I’m Dr. Brandial Bright, also known as the AVangelist. As a dedicated and passionate researcher in autonomous and electric vehicles (AVs and EVs), my mission is to educate and raise awareness within the automotive industry. As the Founder and Managing Partner of Fifth Level Consulting, I promote the adoption and innovation of advanced vehicle technologies through speaking engagements, consulting, and research as we progress to level 5 fully autonomous vehicles.